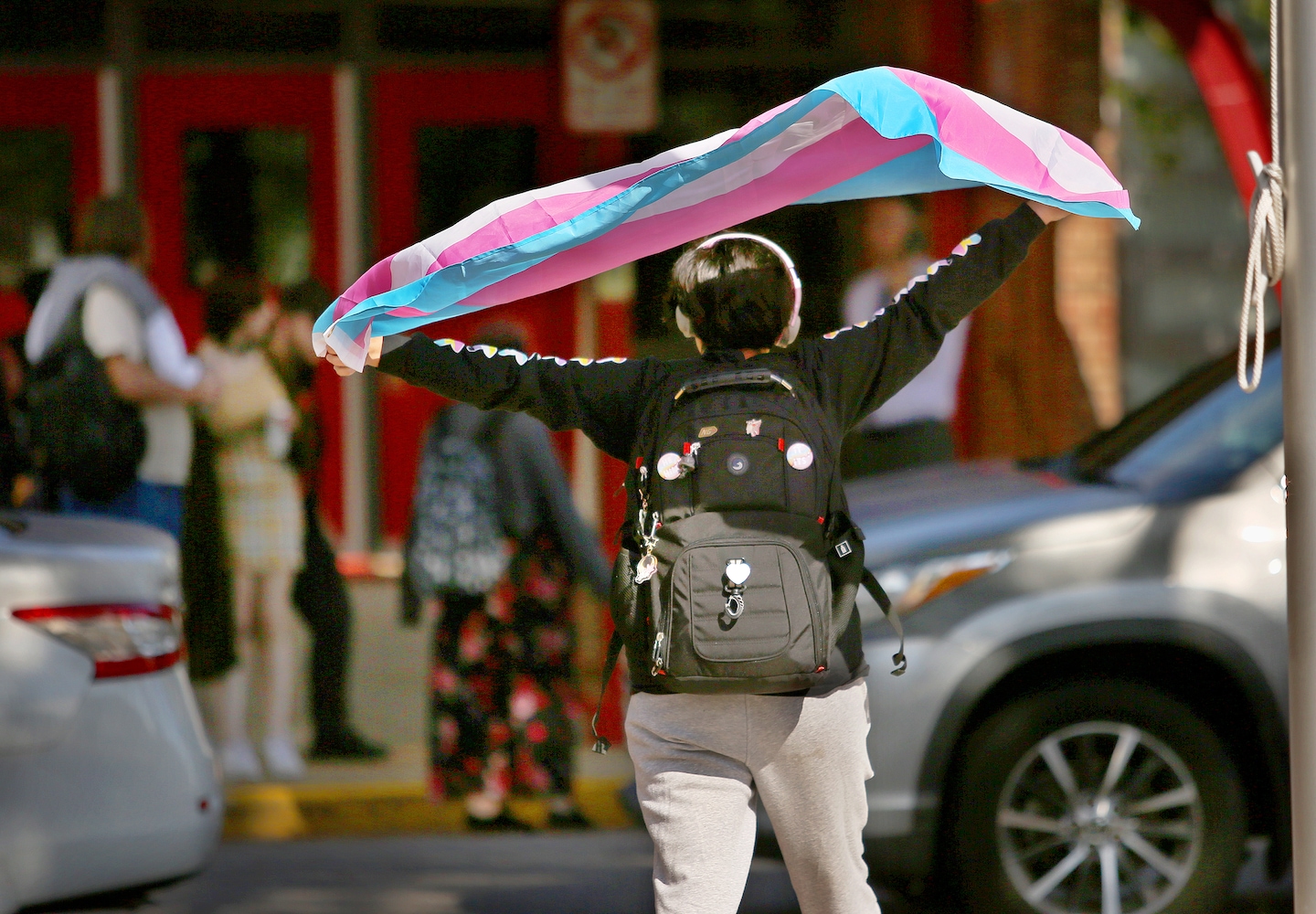
The Biden administration on Friday finalized sweeping new rules barring schools from discriminating against transgender students and ordering significant changes for how schools adjudicate claims of sexual harassment and assault on campus.
The provisions regarding gender identity are the most politically fraught, setting up an election-year culture clash with conservative states and school boards that have limited transgender rights in schools, banned discussion of gender identity in classrooms and removed books with LGBTQ+ themes. Mindful of the politics, the administration is delaying action on the contentious issue of whether transgender girls and women should be allowed to compete in women’s and girls’ sports.
The long-awaited regulation represents the administration’s interpretation of Title IX, a 1972 law that bars sex discrimination in schools that receive federal funding. Title IX is best known for ushering in equal treatment for women in sports, but it also governs how schools handle complaints of sexual harassment and assault, a huge issue on many college campuses.
Now the Biden administration is deploying the regulation to formalize its long-standing view that sex discrimination includes discrimination based on gender identity as well as sexual orientation, a direct challenge to conservative policies across the country.
Ten states, for instance, require transgender students to use bathrooms and locker rooms that align with their biological sex identified at birth, according to tracking by the Movement Advancement Project. Some school districts will not use the pronouns corresponding with a trans student’s gender identity. Both situations might constitute violations of Title IX under the new regulation. In addition, if a school failed to properly address bullying based on gender identity or sexual orientation, that, too, could be a violation of federal law.
“No one should face bullying or discrimination just because of who they are or who they love. Sadly, this happens all too often,” Education Secretary Miguel Cardona told reporters in a conference call.
The Education Department’s Office for Civil Rights investigates allegations of sex discrimination, among other things, and schools that fail to come into compliance risk losing federal funding. A senior administration official said that the office could investigate cases where schools were potentially discriminating, even if they were following their own state’s law.
The final regulation also includes provisions barring discrimination based on pregnancy, including childbirth, abortion and lactation. For instance, schools must accommodate students’ need to attend medical appointments, as well as provide students and workers who are nursing a clean, private space to pump milk.
The combination of these two issues — sexual assault and transgender rights — drew enormous public interest, with some 240,000 public comments submitted in response to the proposed version published in 2022. The new rules take effect Aug. 1, in time for the start of next school year.
The final regulation unravels a Trump-era system for handling sexual assault complaints, discarding some of the rules that bolstered due process rights of the accused. Supporters said those rules were critical to ensuring that students had the opportunity to defend themselves; critics said they discouraged sexual assault survivors from reporting incidents and turned colleges into quasi-courtrooms.
Education Department officials said they had retained the elements that made sense but created a better overall framework that gave equal treatment and balanced the rights of all involved. “A fair process will help ensure that investigations lead to accurate, reliable and effective resolution of sex discrimination complaints,” Cardona said.
Under the Trump administration’s regulation, finalized in 2020, colleges were required to stage live hearings to adjudicate complaints, where the accused could cross-examine witnesses — including the students who were alleging assault. Supporters said that live hearings were critical to ascertaining what actually happened when facts are contested, but others argued cross-examination could retraumatize assault survivors.
Under the new Biden rules, colleges will have more flexibility. The investigator or person adjudicating the case may question witnesses in separate meetings or employ a live hearing.
The new rules also will allow schools to use a lower bar for adjudicating guilt. In weighing evidence, they are now directed to use a “preponderance of the evidence” standard, though they may opt for a higher standard of “clear and convincing evidence” if they use that standard in other similar proceedings. Under the Trump version, universities had a choice, but they were required to use the higher standard if they did so in other settings.
The proposal also expands the definition of what constitutes sexual harassment, discarding a narrower definition used under President Donald Trump, and broadens who on campus has a responsibility to respond to allegations.
Some of the Trump provisions were retained. Schools, for instance, will continue to have the option to use informal resolution of discrimination complaints, unless the allegation involves an employee of a K-12 school.
The Biden administration’s approach was welcomed by advocates for sexual assault survivors.
The rules “will make schools safer and more accessible for young people, many of whom experienced irreparable harm while they fought for protection and support,” said Emma Grasso Levine, senior manager of Title IX policy and programs at Know Your IX, a project of the advocacy group Advocates for Youth.
“Now, it’s up to school administrators to act quickly to implement and enforce” the new rules, she added.
Sexual assault has been a serious issue on college campuses for years, and in releasing the regulation, the Biden administration said the rates were still “unacceptably high.”
But the most controversial element of the regulation involves the rights of transgender students, and it came under immediate fire.
Administration officials point to a 2020 Supreme Court ruling that sex discrimination in employment includes gender identity and sexual orientation to bolster their interpretation of the law. But conservatives contend that Title IX does not include these elements and argue that accommodations for transgender students can create situations that put other students at risk. They object, for instance, to having a transgender woman — someone they refer to as a “biological man” — using women’s bathrooms or locker rooms.
Rep. Virginia Foxx (R-N.C.), chairwoman of the House Education Committee, called the regulation an escalation of Democrats’ “contemptuous culture war that aims to radically redefine sex and gender.” The department, she said, has put decades of advancement for women and girls “squarely on the chopping block.”
“Evidently, the acceptance of biological reality, and the faithful implementation of the law, are just pills too big for the Department to swallow — and it shows,” she said in a statement.
Still, the administration sidestepped the contentious issue of athletics, at least for now. A separate regulation governing how and when schools may exclude transgender students from women and girls teams remains under review, and administration officials offered no timetable for when it would be finalized. People familiar with their thinking said it was being delayed to avoid injecting the matter into the presidential campaign, where President Biden faces a close race against Trump.
A senior administration official, who spoke on the condition of anonymity in a briefing with reporters Thursday, declined to comment on the politics of this decision but noted that the athletics rule was proposed after the main Title IX regulation.
Polling shows that clear majorities of Americans, including a sizable slice of Democrats, oppose allowing transgender athletes to compete on girls’ and women’s teams. Twenty-five states have statewide bans on their participation.
The proposed sports regulation disallows these statewide, blanket bans, but it allows school districts to restrict participation more narrowly defined — for instance on competitive high school or college teams. The main Title IX regulation does not address the issue, and an administration official said the status quo would remain. Still, some have argued that the new general ban on discrimination could apply to sports even though the administration does not intend it to.
The rules governing how campuses deal with harassment complaints have changed repeatedly in recent years.
The Obama administration issued detailed guidance in 2014 for schools in handling complaints, but that was later tossed out by Trump Education Secretary Betsy DeVos. Her department went through its own laborious rulemaking process to put a new system in place.
As a candidate for president in 2020, Biden promised to put a “quick end” to that version if elected, saying it gave colleges “a green light to ignore sexual violence and strip survivors of their rights.” Friday’s action makes good on his promise.
Danielle Douglas-Gabriel contributed to this report.



